High blood pressure overview
High blood pressure (hypertension) occurs when the force of your blood pushing against the walls of your blood vessels is too high.
This is a very frequent condition, affecting just under 50% of the US population.
Unfortunately, many hypertensive patients are either unaware of their condition or are insufficiently treated.
Dr. Leandro Perez discusses high blood pressure and how it can lead to heart disease.
What causes high blood pressure?
High blood pressure develops over time due to an unhealthy lifestyle and lack of regular physical activity. Some conditions, such as diabetes and obesity, can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure. It can also occur during pregnancy.
Symptoms of high blood pressure
Unfortunately, high blood pressure demonstrates no symptoms or warning signs. Most patients won’t even know they have it. The best way to determine elevated blood pressure is to measure yours regularly.
In some cases, hypertension can cause symptoms related to a delayed consequence of long-term high blood pressure. These may include chest pain, shortness of breath, ankle swelling, headaches, visual disturbances, leg discomfort and others.
How is high blood pressure diagnosed?
Blood pressure is measured with an instrument called sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff); it measures your blood pressure reliably. This measurement is performed at your doctor’s office and also is available at multiple point of care locations such as pharmacies, grocery stores. Additionally, modern devices are commercially available and are used at home for keeping blood pressure logs.
How is high blood pressure managed?
It’s entirely possible to lower your blood pressure into a healthy range by making the appropriate lifestyle changes. As much as possible, get at least 30 minutes of physical activity per day. If you have a bit of a sweet tooth, it’s time to trim down. Limit your intake of alcohol and sodium as well. Finally, manage your stress by getting enough sleep and eliminating stressors.
Medications to treat high blood pressure are widely available and are very effective at controlling your blood pressure.
Treating high blood pressure
Dr. Leandro Perez shows how you can control high blood pressure through healthy lifestyle habits and taking medicines, if needed.
To request a consultation click below or call (239) 300–0586
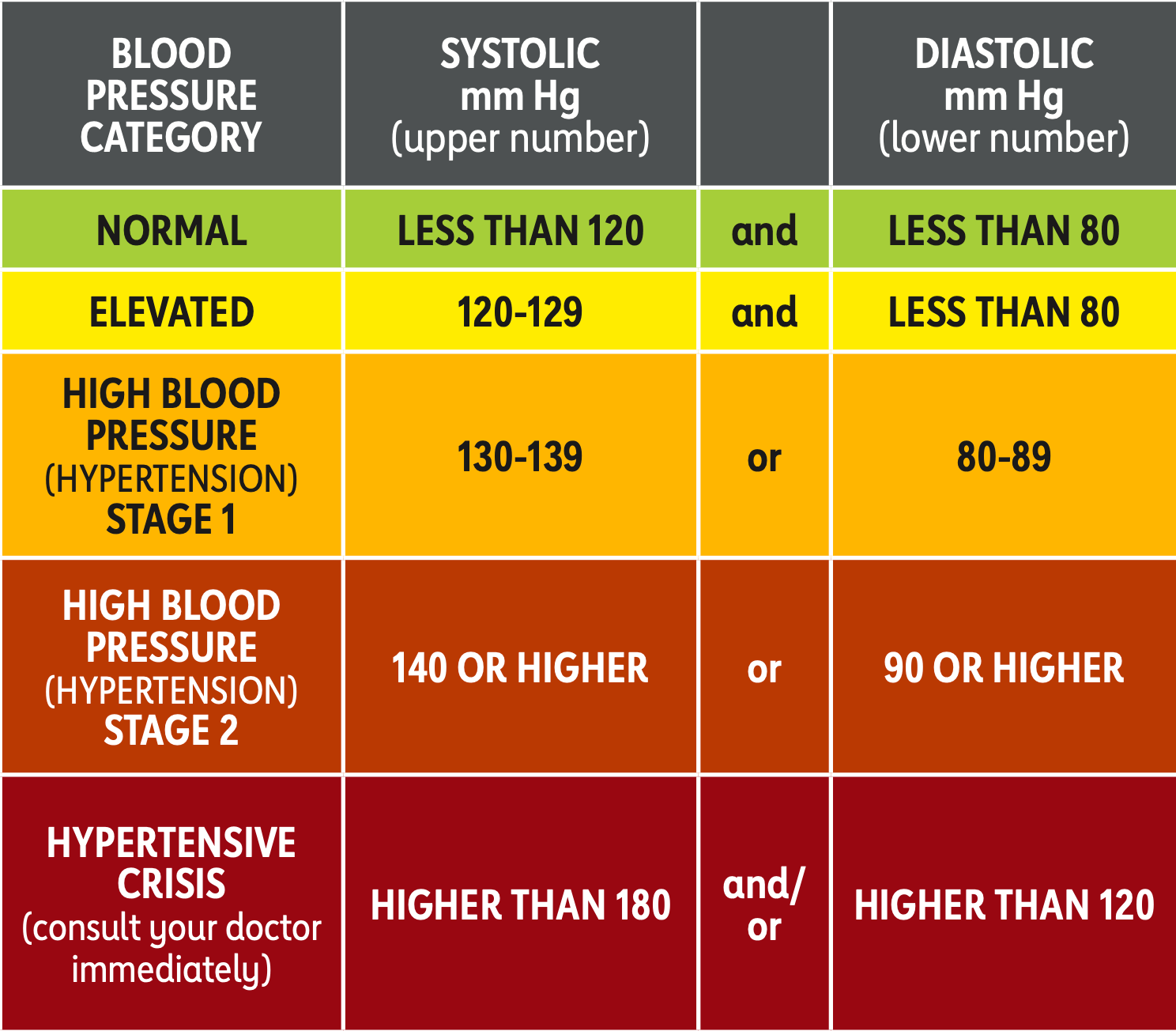
Your blood pressure reading is recorded as two numbers
Systolic blood pressure (the top number): indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls during heartbeats.
Diastolic blood pressure (the bottom number): indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting between beats.
Blood Pressure Categories
According to the American Heart Association, if your blood pressure is normal (120 mm Hg) then you should be screened for high blood pressure once every two years.
To request a consultation click below or call (239) 300–0586